-
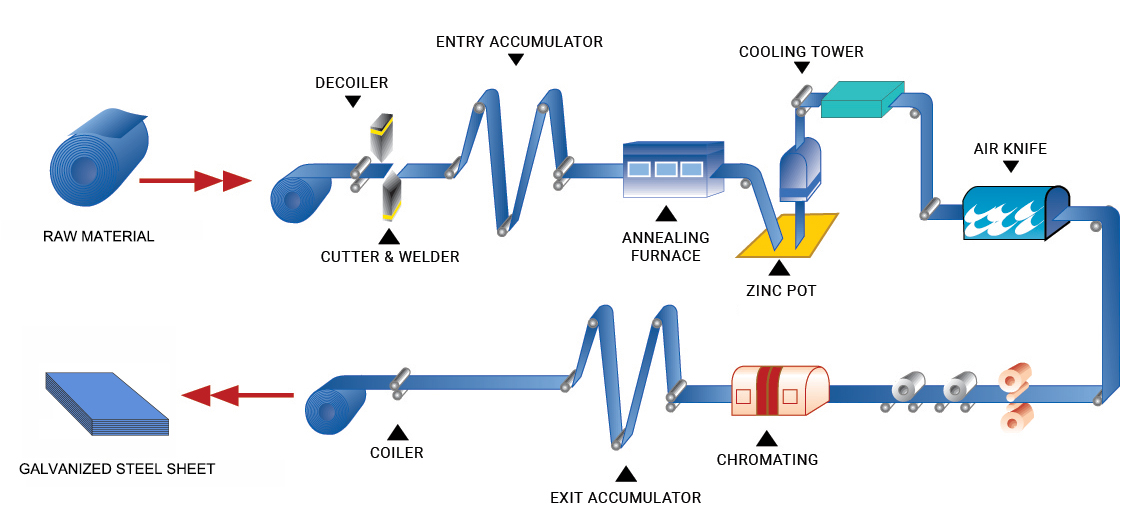
Processo di galvanizzazione
La galvanizzazione si riferisce al processo di applicazione di un strato di zinco sulla superficie metallica per migliorarne la resistenza alla corrosione. Di seguito sono indicati i principali processi della galvanizzazione:
1. Ispezione dei materiali grezzi: Verificare la qualità dei materiali da galvanizzare per assicurarsi che rispettino i requisiti del processo.
2. Acidificazione: Usare acido per rimuovere lo scala di ossido ferroso e altre impurità dalla superficie delle parti in acciaio.
3. Pulizia: Dopo l'acidificazione, le parti in acciaio vengono pulite accuratamente per rimuovere gli acidi residui e altri contaminanti.
4. Assistenza al zinco: Applicare uno strato di solvente contenente cloruro di zinco o un miscuglio di cloruro di ammonio e cloruro di zinco sulla superficie delle parti in acciaio pulite per prevenire l'ossidazione delle parti in acciaio.
5. Asciugatura: Mettere le parti in acciaio rivestite di solvente nel forno di asciugatura per un migliore processo successivo di galvanizzazione.
6. Galvanizzazione: Immergere le parti di acciaio asciutte nel liquido di zinco fuso per far aderire uniformemente il rivestimento di zinco alla superficie delle parti in acciaio.
7. Raffreddamento: Dopo la galvanizzazione, le parti in acciaio vengono raffreddate rapidamente per fissare la struttura del rivestimento di zinco.
8. Passivazione: Formare un film protettivo sulla superficie dell'acciaio per impedire che il rivestimento di zinco venga ulteriormente ossidato.
9. Pulizia: Infine, pulire l'acciaio per rimuovere eventuali residui presenti sulla superficie.
10. Ispezione finale del prodotto: Eseguire un'ispezione finale della qualità sull'acciaio galvanizzato per assicurarsi che il prodotto rispetti gli standard.
11. Ispezione e imballaggio: Imballare i prodotti qualificati e prepararli per la consegna. Ciò che precede è il processo di base del galvanizzazione. Si noti che diversi processi di galvanizzazione possono avere alcune differenze nei dettagli, ma il processo complessivo è simile.
Guarda il video -
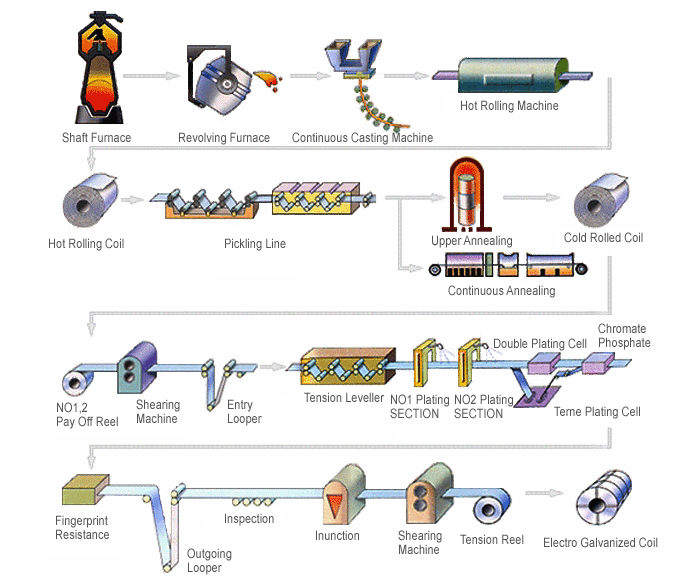
Acciaio elettrogalvanizzato
1. Processo di ingresso: L'attrezzatura all'ingresso della linea di galvanizzazione include bobina di prelievo, macchina da taglio, macchina da saldatura, arrotolatore e livellatore a tensione. La bobina trasmette i materiali in acciaio impilati o a freddo al laminatoio, che taglia e connette i materiali pronti per l'unione. Segue quindi la saldatura.
2. Processo di pre-trattamento: La linea di pulizia elettrolitica è composta da una vasca elettrolitica, una vasca di acidificazione e una vasca di sciacquatura, utilizzate per rimuovere contaminanti e film ossidici dalla superficie dell'acciaio prima della galvanizzazione.
3. Elettrogalvanizzazione: Il metodo CAROSEL, come altri metodi di elettrogalvanizzazione, prevede l'elettroplaccatura di un lato alla volta attraverso un rullo conduttore. Il processo produce lastre doppie singole con rivestimento differenziale. Esistono anche tipi orizzontali, in cui entrambi i lati della lastra vengono elettroplaccati contemporaneamente per produrre lastre doppie rivestite.
4. Rivestimento a base di fosfato: Un rivestimento a base di fosfato viene applicato sulla superficie del strato di zinco tramite reazione chimica o elettrochimica. Il rivestimento ha lo scopo di fornire una protezione temporanea contro la corrosione e di produrre un substrato sicuro da imprimere.
5. Trattamento anti-impronte digitali: un film organico, inorganico o ibrido organico-inorganico viene applicato sulla superficie della lastra di acciaio per integrare la sua resistenza alla corrosione e migliorare le proprietà richieste, come la marcatura anti-impronte digitali e la lavorabilità .
6. Processo di uscita: Il punto di uscita della linea di produzione include bobina di uscita, bobina di tensione e linea di imballaggio automatica per proteggere il prodotto dopo l'avvolgimento.
Guarda il video

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 SQ
SQ
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 MT
MT
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 GA
GA
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 HY
HY
 AZ
AZ
 KA
KA
 BN
BN
 BS
BS
 LO
LO
 MN
MN




