-
Stainless steel production process
Stainless steel production mainly includes crude steel smelting, hot rolling, cold rolling and other links. The following is a popularization of the stainless steel production process:
1. Stainless steel crude steel smelting process
At present, the smelting processes for producing stainless steel in the world are mainly divided into one-step, two-step and three-step methods, as well as new integrated production methods. One-step smelting is: molten iron + AOD (argon oxygen refining furnace); two-step method is: EAF (electric arc furnace) + AOD (argon oxygen refining furnace). The three-step method is: EAF (electric arc furnace) + AOD (argon oxygen refining furnace) + VOD (vacuum refining furnace). In addition to several traditional production processes, the current integrated production process, that is, the production process from molten iron directly to stainless steel, is also adopted by many companies. The production process is: RKEF (rotary kiln electric furnace) + AOD (argon oxygen refining furnace).
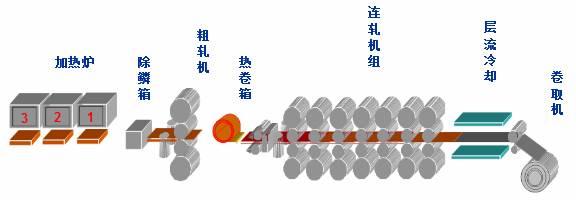
2. Stainless steel hot rolling process
The hot rolling process of stainless steel uses slabs (mainly continuous casting slabs) as raw materials, and after heating, it is made into strip steel by rough rolling units and finishing units. The hot steel strip coming out of the last rolling mill of the finishing rolling is cooled to the set temperature through laminar flow and rolled into a steel coil by the coiler. The cooled steel coil has an oxide scale on the surface and is black, commonly known as "stainless steel black coil". After annealing and pickling, the oxidized surface is removed, which is the "stainless steel white coil". Most of the hot-rolled products circulating in the stainless steel market are stainless steel white coils. The specific stainless steel hot rolling production process is as follows:
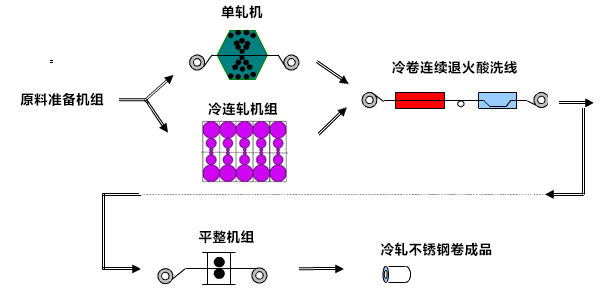
3. Stainless steel cold rolling process
After hot rolling of stainless steel, some hot-rolled stainless steel products are directly used by downstream, and some hot-rolled products need to be further processed into cold rolling before use.
Stainless steel cold rolling mostly uses hot-rolled stainless steel products with a thickness of 3.0-5.5mm. After rolling processing of cold rolling equipment, it is produced into stainless steel cold rolled products. At present, there are two main production processes for stainless steel cold rolling: single-frame cold rolling of stainless steel and multi-frame cold rolling of stainless steel. The specific production process is as follows:
After cold rolling of stainless steel, it needs to go through annealing and pickling units. Annealing of stainless steel after cold rolling is to eliminate work hardening through the process of recrystallization to achieve the purpose of softening; the purpose of pickling is to remove the oxide layer formed on the surface of the steel strip during the annealing process, and to passivate the surface of the stainless steel to improve the corrosion resistance of the steel plate.
View Video -
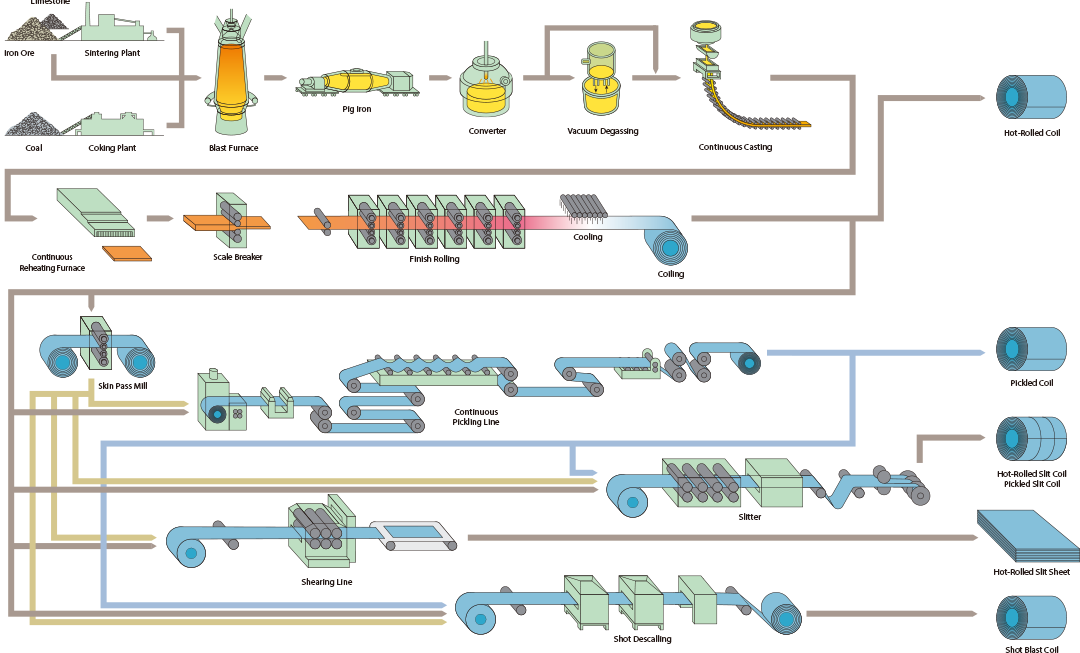
Hot Rolled Steel production process
1.Billet heating: The cold billet is heated to a suitable rolling temperature through a heating furnace. The heating temperature depends on factors such as the composition, shape and rolling requirements of the steel. Rough rolling: The heated billet is fed into the rough rolling unit and rolled through multiple sets of rollers at high temperature. The purpose of rough rolling is to preliminarily adjust the cross-sectional shape and size of the billet to close to the target requirements. Intermediate rolling: The billet after rough rolling is fed into the intermediate rolling unit for further rolling to further adjust the cross-sectional shape.
2.The hot rolling annealing process: refers to the annealing of the metal material after hot rolling to eliminate its internal stress and improve its ductility and toughness. Its basic process is as follows: Hot rolling: The metal material is processed at high temperature to deform it to a predetermined size and shape. Pickling: Impurities such as rust on the metal surface after hot rolling are removed by pickling.
3.Finishing rolling: The purpose of finishing rolling is to adjust the thickness and width of the coil to the specified size and produce a smooth surface and shape at an appropriate finishing temperature to suit its intended use. Our latest equipment, including work conversion mills, double cross mills and online roll grinders (ORG), improve the productivity of the plant and the quality of finished coils by controlling the crown shape.
4.Run-Out Table and Coiling: Steel strips, after the finishing mill, are passed to the run-out table where they are coiled. While being rolled on the table, the strips are sprayed with water to cool them to the proper temperature for coiling.
View Video -
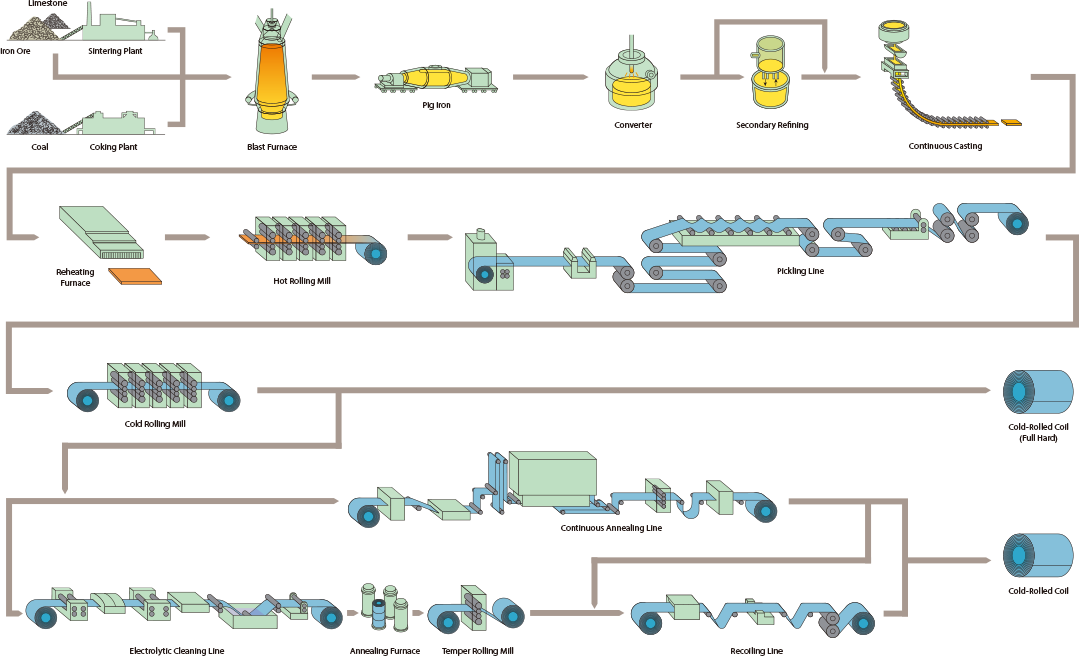
Cold Rolled Steel production process
The process flow of cold-rolled steel sheets includes billet annealing, storage, rust removal, coiling, pickling, cold rolling, pickling liquid modification, steel strip shearing, tempering and final packaging.
1. The steel coils sent from the hot-rolled strip mill are cooled and stored in the steel coil warehouse in front of the pickling unit according to the type and specification, and then the steel coils are sent to the steel coil conveyor in the pickling unit feeding section according to the plan.
2. Uncoil, weld, mechanically descale and soak in the pickling tank in the unit to remove the iron oxide scale on the surface of the strip steel and rinse it. Most of the strip steel needs to be further rolled and treated without end, while the conventionally rolled strip steel is not purified and oiled afterwards.
3. When the cold-rolled sheet is rolled without end, the steel coil is stored through a looper. When conventional rolling is adopted, the steel coil is uncoiled on the uncoiler in the feeding section, and the strip steel is passed through each frame for rolling in turn. The coiler in the discharge section re-rolls the steel into coils and sends them to different units for processing according to different products.
4. Annealing and leveling. For most common purposes, deep drawing and special drawing cold-rolled sheets, they are annealed in a vertical furnace to improve the mechanical properties of the strip. When leveling the cold-rolled sheet, a leveling agent can be sprayed for wet leveling, or dry leveling can be used. Generally, the leveling amount is less than 3%. After leveling, the mechanical properties and quality of the strip are further improved. Some cold-rolled sheets are unrolled and welded in a continuous annealing furnace, stored in a looper, and then surface treated and cleaned, and continuously enter the vertical furnace for annealing. After coming out of the annealing furnace, they are leveled again, trimmed after straightening, and rolled into steel coils according to the specified weight, and sent to the intermediate warehouse for storage by a conveyor.
View Video -
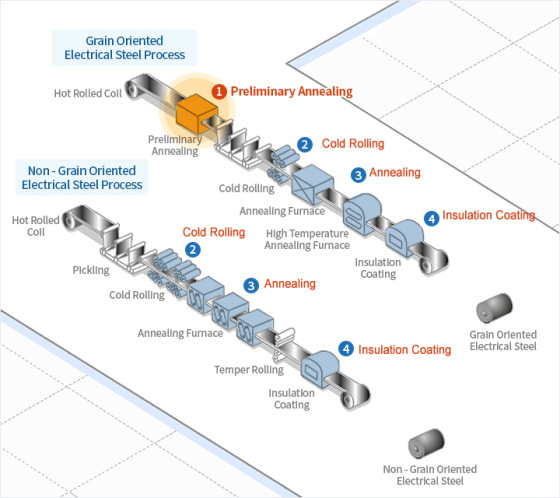
Normalizing process of non-oriented and oriented silicon steel
Silicon steel is a soft magnetic material and the most widely used alloy material among magnetic materials. According to the arrangement direction of the grains in the product, it is divided into grain-oriented silicon steel and grain-non-oriented silicon steel. High-grade and high-efficiency non-oriented silicon steel and high-magnetic induction oriented silicon steel must be normalized during the production process to achieve the required grain texture and magnetic properties.
1.Normalization production process of non-oriented silicon steel: 1. The strip steel is heated to 1000℃ after the preheating non-oxidation section; 2. The radiation tube heating section, heating/cooling section, and soaking section are all used as soaking sections for normalization treatment; 3. The 2# heating/cooling section is used as the cooling section in the furnace to cool the strip steel to 850℃; 4. The air wiper, mist cooling section, and 1# water spray section are used as the first slow cooling section outside the furnace to cool the strip steel to below 750℃; 5. The water jacket cooling section is used as the second slow cooling section outside the furnace to cool the strip steel to below 600℃; 6. The 2# water spray cooling section is used as the fast cooling section to cool the strip steel to below 80℃.
2.Normalization production process of oriented silicon steel: 1. The strip steel passes through the preheating non-oxidation section and is heated to 1100℃; 2. Passes through the radiation tube heating section and is heated to 1120℃; 3. Passes through the 1# heating/cooling section and is cooled to 950℃; 4. The equalization section and the 2# heating/cooling section are both used as equalization sections for normalization treatment; 5. Rapidly cools to 550℃ in the mist cooling section; 6. Finally cools to below 80℃ in the 1# water spray section.
3.Research on reducing steel loss of oriented silicon steel. The main measures to further reduce the iron loss of oriented silicon steel include refining the magnetic domain (which is more effective in reducing the iron loss of Hi-B steel and products with a thickness of ≤0.23mm), increasing the silicon content, reducing the thickness of the steel plate, and reducing the size of the secondary recrystallized grains. Since the silicon content in silicon steel is too high, it is easy to cause the cold workability to deteriorate, so the degree of reducing the iron loss by increasing the silicon content is limited. Therefore, the main goal of reducing iron loss is to refine the magnetic domain and reduce the thickness of the steel plate.
4.The heating temperature of the steel ingot is required to be 1360~1380℃ (the solid solution temperature of MnS in the equilibrium state is 1320℃).
View Video -
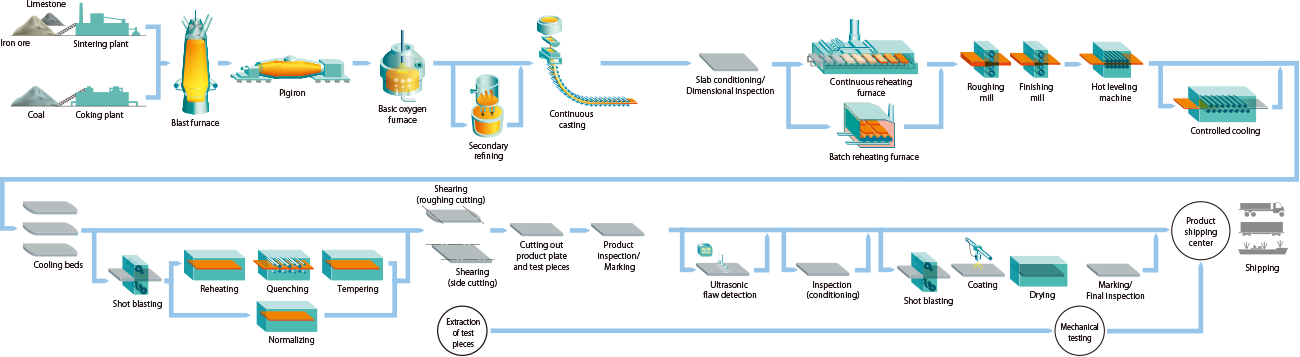
Steel plate manufacturing process flow
Mainly includes the following steps:
1. Coking production process: Coking operation is the process of mixing and crushing coking coal into the coking furnace and then distilling it to produce hot coke and coke oven gas.
2. Sintering production process: Sintering operation is to mix and granulate powdered iron ore, various fluxes and fine coke, and then add them to the sintering machine through the distribution system. The fine coke is ignited by the ignition furnace, and the sintering reaction is completed by exhausting the air through the exhaust windmill. The high-temperature sintered ore is crushed, cooled, and screened, and then sent to the blast furnace as the main raw material for smelting molten iron.
3. Blast furnace production process: Blast furnace operation is to add iron ore, coke and flux into the furnace from the top of the blast furnace, and then blow high-temperature hot air from the blast nozzle at the bottom of the furnace to produce reducing gas, reduce iron ore, and produce molten iron and slag.
4. Converter production process: The steel mill first sends the melted milling to the pre-treatment station for desulfurization and dephosphorization. After the converter blowing, it is sent to the secondary refining treatment station (RH vacuum degassing treatment station, LadleInjection ladle blowing treatment station, VOD vacuum oxygen blowing decarburization treatment station, STN mixing station, etc.) for various treatments according to the characteristics and quality requirements of the ordered steel type, and the composition of the molten steel is adjusted. Finally, it is sent to the large steel billet and flat steel billet continuous casting machine to be cast into red-hot steel billet semi-finished products. After inspection, grinding or burning off surface defects, it can be directly sent to the downstream for rolling into finished products such as strip steel, wire rod, steel plate, steel coil and steel sheet.
5. Continuous casting production process: Continuous casting operation is the process of converting molten steel into steel billets. The molten steel that has been processed upstream is transported to the turntable in a steel ladle, divided into several strands by a molten steel distributor, and injected into a mold of a specific shape. It begins to cool and solidify to form a cast embryo with a solidified shell on the outside and molten steel on the inside. The cast embryo is then drawn into an arc-shaped casting channel and continues to solidify after secondary cooling until it is completely solidified. After straightening, it is cut into blocks according to the order length. The square shape is the large steel embryo, and the plate shape is the flat steel embryo. This semi-finished product is sent to the rolling mill for rolling after the surface treatment of the steel embryo as needed.
6. Small billet production process: The large steel embryo is produced by the continuous casting machine and is heated, rust-removed, burned, rough-rolled, fine-rolled, and sheared to produce a small steel embryo with a cross-section of 118mm×118mm. 60% of the small steel embryos are then inspected and ground to remove surface defects and supplied to the bar and wire factories for rolling into bar steel, wire coils and straight bar steel products.
7. Hot-rolled steel production process: Hot rolling means that the material needs to be heated during or before rolling. Generally, it is rolled only after heating to above the recrystallization temperature. Features of hot-rolled products: Hot-rolled products have excellent properties such as high strength, good toughness, easy processing and forming, and good weldability, so they are widely used in manufacturing industries such as ships, automobiles, bridges, buildings, machinery, and pressure vessels.
8. Wire production process: The wire factory production operation is to heat the small billet in the heating furnace, and then roll it through the rough rolling unit, the intermediate rolling unit, the finishing mill, and the reducing forming machine, and then coil it through the coiling machine, and then convey it on the cooling conveyor belt and send it to the finishing area for finishing.
9. Steel plate production process: The steel plate production operation uses flat billets as raw materials. The flat billets are heated to 1200°C in the heating furnace, and then rolled, cooled, leveled, and sheared (flamed) to become finished products. The above is the main process flow of steel plate manufacturing. It should be noted that different steel plates may require additional processing, such as surface treatment, heat treatment, etc., to meet specific application requirements.
View Video

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 SQ
SQ
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 MT
MT
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 GA
GA
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 HY
HY
 AZ
AZ
 KA
KA
 BN
BN
 BS
BS
 LO
LO
 MN
MN




